A Theory's Ability to Explain Several Different Observations Is Its
Gardners theory of multiple intelligences has had an important impact on how we think about human intelligence. It is often modified to reconcile new facts but it can also become obsolete when a new scientific theory is proposed that can explain more observations and facts than the previous one.
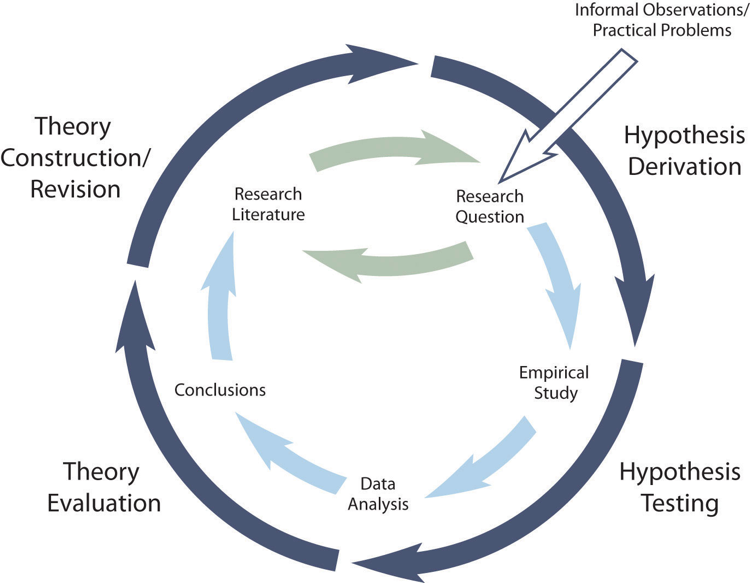
Using Theories In Psychological Research Research Methods In Psychology 2nd Canadian Edition
Allows interpretation and must account for data-theories imply observations-explain law Hypothesis is an educated guess that involves two or more variables and is testable and falsifiable Laws are more definitive with substantial evidence.
. Darwins observations that led to his theory of natural selection are. The theory will not be proven incorrect later on. Experiential learning theory or ELT was identified by David Kolb in 1984.
A scientific theory is a substantiated and testable explanation for a variety of observations and facts. Although there is no formula for effective leadership many theories have developed to explain the leadership process at its best. If many different observations can all be explained by the same theory does that make the theory true.
Theories cannot help predict what may happen in the future. Paradigms Theory Research and Ethnics of Social Research What are the functions of theory. Variation there are variations between members of the same species.
Watson Ivan Pavlov and B. Many of us are familiar with three broad categories in which people learn. Does it make the theory more likely.
These theories deal only with observable behaviors. In Darwins observations of the finches in the Galapagos Islands he noticed that each island had a different type of finch but they all were similar to the finch species in. Theories explain observations and hypotheses.
The theory has been disconfirmed. What five observations led to Darwins theory of natural selection. Theories are used by scientists to generate research and organize observations.
A phenomenon plural phenomena is a general result that has been observed reliably in systematic empirical researchIn essence it is an established answer to a research question. Theories may be scientific belong to a non-scientific discipline or no discipline at all. Something other than a useful scientific concept.
Since then differential association theory has remained popular in the field of criminology and has sparked a great deal of research. Theories result from several repeated experiments. Some phenomena we have encountered in this book are that expressive writing improves health women do not talk more than men and cell phone usage impairs driving ability.
Adaptation traits that increase suitability to a species. One is not more important than the other but some may help people succeed at different things. Development is considered a reaction to rewards punishments stimuli and reinforcement.
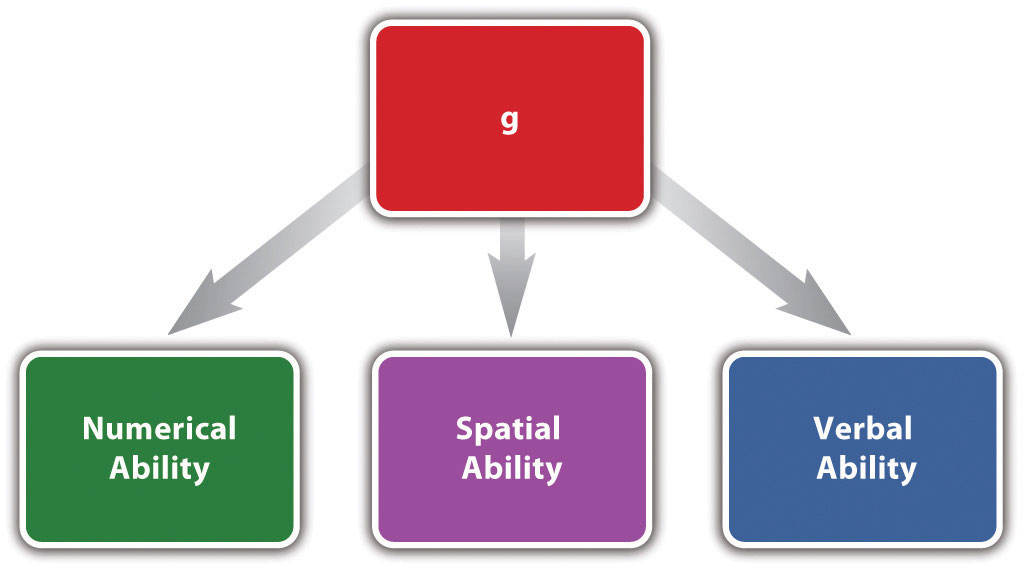
Rather than simply focusing on a single measure of human cognitive ability it can be helpful to consider all of the different mental strengths that an individual may possess. Overproduction all species will produce more offspring than will survive to adulthood. This problem has been solved.
Ability to generate research and organize observations. Theories are based on a single hypothesis. You can have more confidence in the theorys ability to explain and predict phenomena within its scope.
Make sense of observed patterns in ways that suggest other possibilities. Depending on the context a theorys assertions. Though his influence came from other theorists such as John Dewey Kurt Lewin and Jean Piaget Kolb was able to identify four stages of ELT.
Howard Gardners Theory of Multiple Intelligences. Beyond these three categories many theories of and approaches toward human learning potential have been established. A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon or the results of such thinking.
A theory is a systematic set of interrelated statements intended to explain some aspect of social life. Theory Defined A theory is a set of related assumptions that allow scientists to use logical deductive reasoning to formulate testable hypotheses. Theories are tools used by scientists to give meaning to observations.
No it cannot be true unless it is proven true or is a proven fact but yes it could be likely because if many observations are all explained by the same theory it could mean it is on its way to being true. The theory must give meaning to data The data should come from experimental research designed to test hypothesis generate by the theory it should generate it explain it and explain other observations in other words both descriptive and hypothesis testing. The theory has been proven correct.
Behavioral theories of child development focus on how environmental interaction influences behavior and is based on the theories of theorists such as John B. The Multiple Intelligences Theory throws away the idea that intelligence is one sort of general ability and argues that there are actually eight types of intelligence. Theory is explanation for unobservable events and involves multiple variables.
Ancient and modern societies alike have been fascinated by the intricacy of dynamic leadership. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Leadership is a process whereby an individual influences a group of individuals to achieve a common goal Bor 2021a.
Visual learning auditory learning and kinesthetic learning. Among them is the theory of multiple intelligences developed. Theories may be revised over time.
It also makes predictions about the future. For example a person with high musical intelligence and low visual-spatial. The word theory is most closely associated with.
The first two stages concrete learning and reflective observation focus on grasping an experience. One of the reasons for the theorys continued pertinence is its broad ability to explain all kinds of criminal activity from juvenile delinquency to white collar crime. Can be explained by several different theories.
Chapter 5 Scientific Progress Introduction To History And Philosophy Of Science

Research Methods Ii Midterm Study Guide

Piaget S Theory Of Cognitive Development Cleverism
Chapter 4 Theories In Scientific Research Research Methods For The Social Sciences

Biological Evolution Notes Biology Vista Overview

Research Methods Ii Midterm Study Guide

Philosophy Of The Sciences Lecture 3 13 09 03 The Demarcation Problem And Falsificationism Ppt Download

Unit 1 1 1 2 2 Notes An Introduction To Psychological Science 3e Canada Version Notes For Studocu
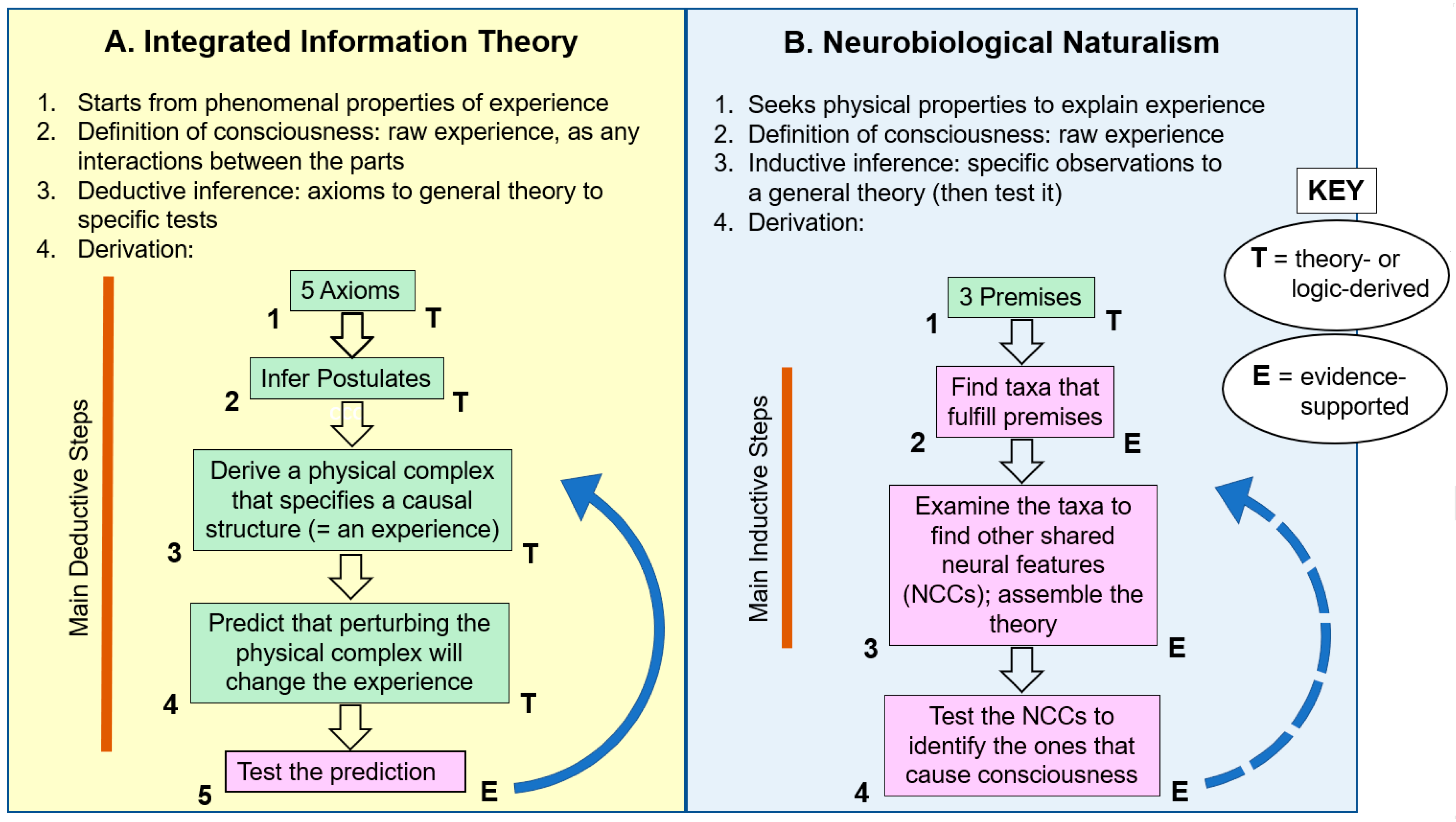
Entropy Free Full Text A Traditional Scientific Perspective On The Integrated Information Theory Of Consciousness Html

Pdf Moving Forward With Activity Theory In A Digital World

Midterm Review Psyc 2100 Introduction To Social Psychology Studocu

What Is String Theory New Scientist
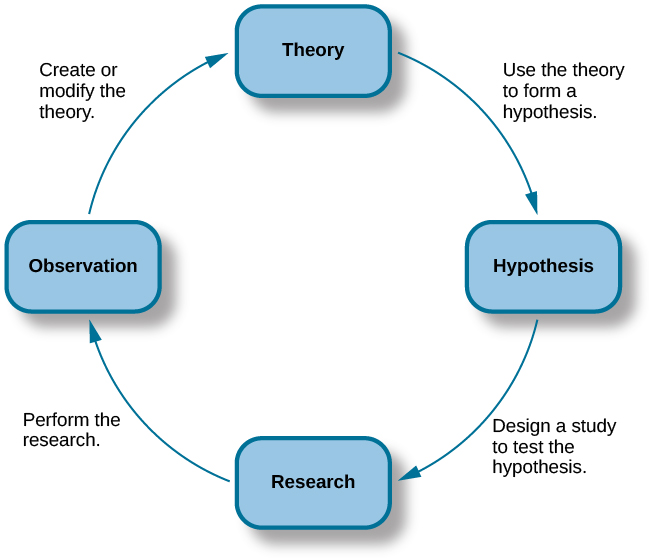
The Scientific Process Introduction To Psychology

Pdf Introduction To Theories Of Personality Stephanie Olino Academia Edu

Pdf Theories Of Mass Communication Hera Cabonegro Academia Edu

Comments
Post a Comment